Cri du chat cry - 🧡 Cri Du Chat Syndrome Article
Recent Posts
- Dječija porno
- Doris dragović porno
- Seks koliko često
- Najveće gole grudi
- Porno seljanke
- Ljubavni filmovi online sa prevodom ceo film
- Ljubavne poruke za nju nedostajes mi
- Bukovski ljubavne pjesme
- Stranice za skidanje porno filmova
- Najljepši ljubavni stihovi
- Erotic model hd porn
- Rusian teen porno
- Bambi blecks porno star
- Chat domain
- Porno seks erotik
- Balka chat
- Je hebt nooit seks gehad
Cri
However, pontine hypoplasia seems to be the most common feature.
Overview: What is Cri
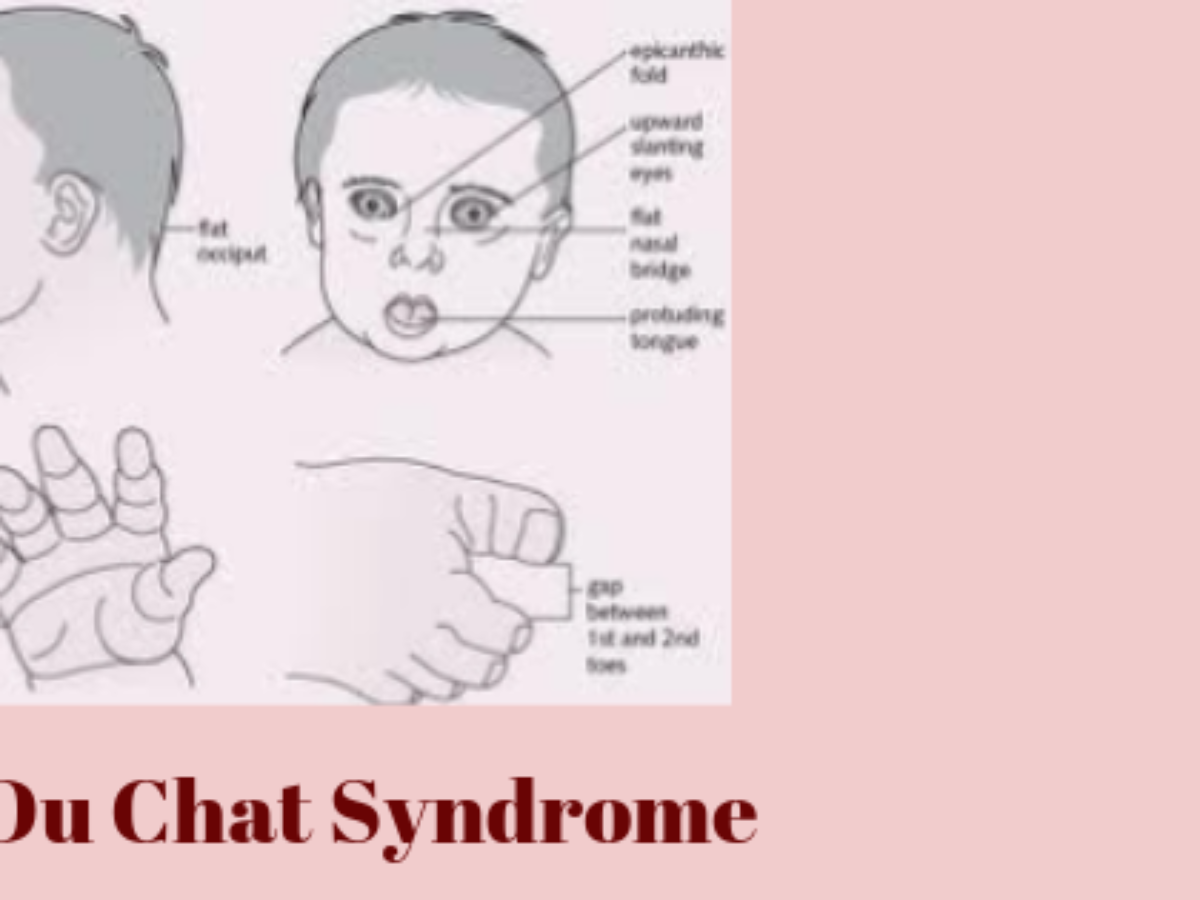
Cri-du-chat syndrome is characterized by intellectual disability and delayed development, small head size microcephaly , low birth weight, and weak muscle tone hypotonia in infancy.
The most common heart defect is patent ductus arteriosus, a condition in which the passage ductus between the blood vessel that leads to the lungs pulmonary artery and the major artery of the body aorta fails to close after birth.
Sometimes this can be difficult because the features may not be obvious as patients show a cytogenetic variation leading to phenotypic variation.
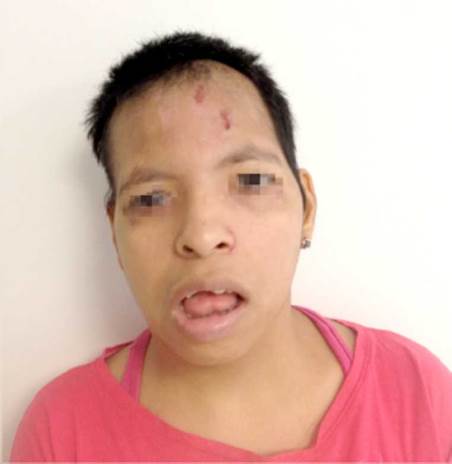
Infants who are born with the syndrome often have a high-pitched cry that sounds like a cat, hence the condition's name.
- Related articles
2022 error.webket.jp










.mp4/544e463222d48Summer - Knot That Lady zooskoolcom - Zootube Zoofilia K9 Vids (1).mp4-3b.jpg)





(mh=2gR2HfTrQCP_3ugp).jpg)










While no one specific test can determine if symptoms are caused by cri du chat syndrome, evidence of particular medical conditions, visual observance of physical abnormalities and testing of behavioral and cognitive functionality can help to determine an appropriate diagnosis.
The size of the deletion varies among affected individuals; studies suggest that larger deletions tend to result in more severe intellectual disability and developmental delay than smaller deletions.
However, patients benefit from rehabilitation, but results are better the earlier it starts.